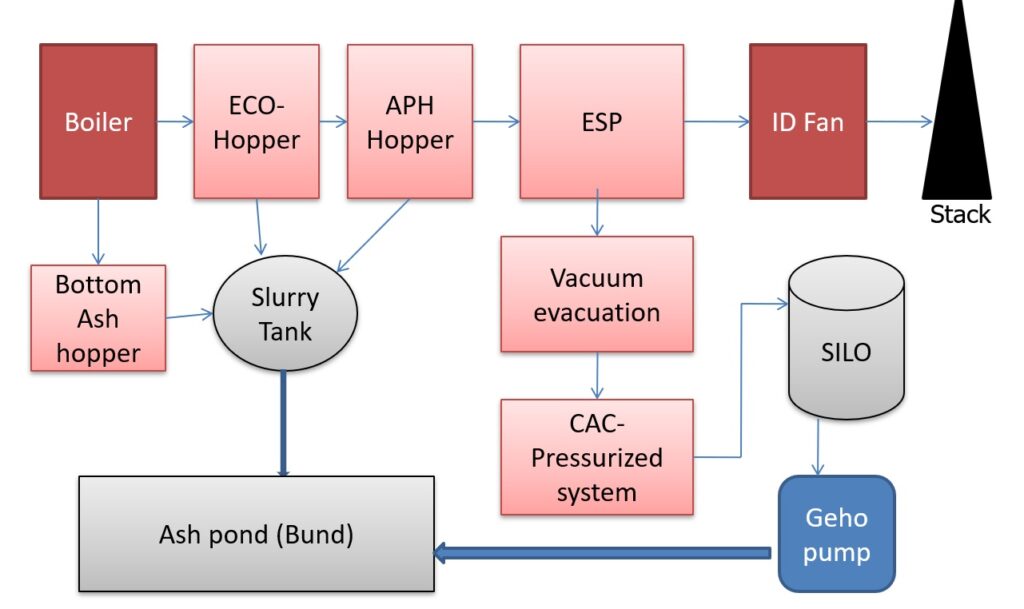
In the article, Microprocessor 8085 program to find the largest number from an array of data in assembly language programming (ALP) is explained.
It is highly recommended to learn the instruction set of 8085 in detail before programming.
Problem:
Find the largest number in a block of data. The length of the block is in memory location 2200H and the block itself starts from memory location 2201H.
Store the largest number in memory location 2300H. Assume that the numbers in the block are all 8-bit unsigned binary numbers.
Algorithm for Program 1:
1) Load the address of the first element of the array in HL pair
2) Move the count to B – reg.
3) Increment the pointer.
4) Get the first data in A – reg.
5) Decrement the count.
6) Increment the pointer.
7) Compare the content of memory addressed by HL pair with that of A – reg.
8) If Carry = 0, go to step 10 or if Carry = 1 go to step 9.
9) Move the content of memory addressed by HL to A – reg.
10) Decrement the count
11) Check for Zero of the count. If ZF = 0, go to step 6, or if ZF = 1 go to next step.
12) Store the largest data in memory.
13) Terminate the program.
Flowchart

Program 1:
LXI H,2200H ; Set pointer for array.
MOV B, M ;Load the Count.
INX H
MOV A, M ; Set 1st element as largest data.
DCR B ; Decrement the count.
LOOP: INX H
CMP M ; If A- reg > M go to AHEAD
JNC AHEAD
MOV A, M ; Set the new value as largest.
AHEAD: DCR B
JNZ LOOP ; Repeat comparisons till count = 0.
STA 2300H ; Store the largest value at 2300.
HLT ; Terminate program execution.
Program 2:
LDA 2200H
MOV C, A ; Initialize counter.
XRA A ; Maximum = Minimum possible value = 0.
LXI H, 2201H ; Initialize pointer.
BACK: CMP M ; Is number> maximum.
JNC SKIP ; Yes, replace maximum.
MOV A, M
SKIP: INX H
DCR C
JNZ BACK
STA 2300H ; Store maximum number.
HLT ; Terminate program execution.
Sample Example:
(2200H) = 04
(2201H) = 34H
(2202H) = A9H
(2203H) = 78H
(2204H) = 56H
Result = (2300H) = A9H.
Recent posts
Related posts:
- Terminology Used in Microprocessor and Microcontroller
- CISC and RISC Processor Architecture
- Von Neumann and Harvard Architecture
- Basics of Microprocessor and Microcontroller
- Introduction to Microprocessor 8085
- Architecture of 8085 Microprocessor
- Pin Diagram of 8085 Microprocessor and Pin Description
- Addressing Modes in 8085 Microprocessor
- Data Transfer Instructions in 8085 Microprocessor
- Arithmetic Instructions in 8085 Microprocessor
- Logical Instructions in 8085 Microprocessor
- Branching instructions in 8085 Microprocessor
- Machine Control Instructions in 8085 Microprocessor
- Timing Diagram of 8085 Instructions
- Stack and Subroutine in 8085 Microprocessor
- Interrupts in 8085 Microprocessor
- Assembler Directives of 8085 Microprocessor
- Simple Data Transfer Program in 8085 Microprocessor
- Microprocessor 8085 Addition and Subtraction Programs
- Programs on Logical Instructions in 8085 Microprocessor
- Multiplication Programs in 8085 Microprocessor
- Division Programs in 8085 Microprocessor
- Introduction to Assembly Language Programming
- 8085 Program to Count Negative Numbers | ALP to Count Negative Numbers
- 8085 Program to Find the Smallest Number in An Array of Data
- 8085 Program to Arrange an Array of Data in Ascending Order
- 8085 Program to Arrange an Array of Data in Descending Order
- 8085 Program to Find the Square of a Number from 0 to 9 Using a Table of Square