Problem:
Write a microprocessor 8085 program to arrange an array of data in ascending order. The length of the block is in memory location 4200H and the block itself starts from memory location 4201H.
Arrange the numbers in ascending order and store them at memory location from 4201H. Assume that the numbers in the block are all 8-bit unsigned binary numbers.
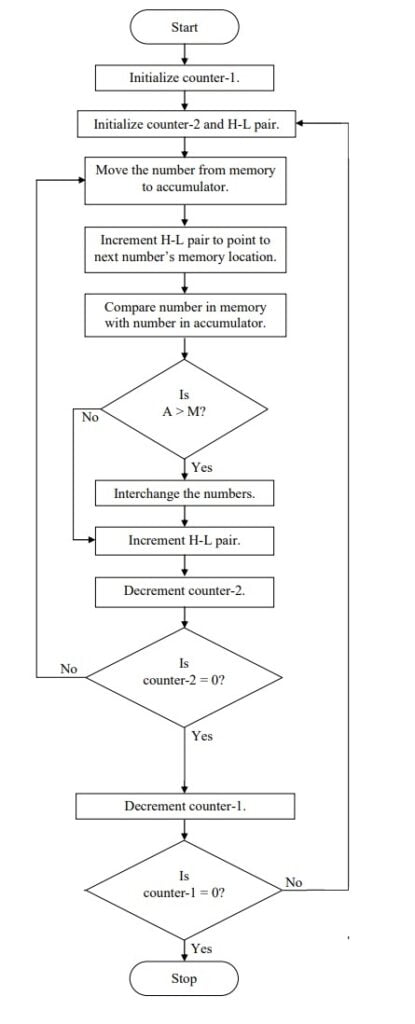
Algorithm:
- Initialize HL pair as memory pointer.
- Get the count at 4200 into C – register.
- Copy it in D – register (for bubble sort (N-1) times required).
- Get the first value in Accumulator.
- Compare it with the value at next location.
- If they are out of order, exchange the contents of Accumulator and Memory.
- Decrement D –register content by 1.
- Repeat steps 5 and 7 till the value in D- register become zero.
- Decrement contents of C –register by 1.
- Repeat steps 3 to 9 till the value in C – register becomes zero.
Flowchart
Program:
LXI H, 4200H ; Set pointer for array.
MOV C, M ; Load the count value.
DCR C ; Decrement counter.
REPEAT: MOV D, C
LXI H, 4201H ; Set the memory pointer for data.
LOOP: MOV A, M ; Move the number into accumulator.
INX H ; Increment memory pointer.
CMP M ; Compare memory and accumulator.
JC SKIP ; jump to skip if carry generated.
MOV B, M ; copy content of memory location to B – Register.
MOV M, A ; copy content of Accumulator to memory location.
DCX H ; Decrement content of HL pair of registers.
MOV M, B ; copy content of B – Register to memory location.
INX H ; Increment content of HL pair of registers.
SKIP: DCR D ; Decrement content of Register – D.
JNZ LOOP ; jump to loop if not equal to zero.
DCR C ; decrement counter.
JNZ REPEAT ; jump to repeat if not equal to zero.
HLT ; Terminate Program.
Sample Example:
Input:
4200 05 (Array Size)
4201 45
4202 DE
4203 17
4204 20
4205 50
Output:
4200 05(Array Size)
4201 17
4202 20
4203 45
4204 50
4205 DE
Recent posts
Related posts:
- Terminology Used in Microprocessor and Microcontroller
- CISC and RISC Processor Architecture
- Von Neumann and Harvard Architecture
- Basics of Microprocessor and Microcontroller
- Introduction to Microprocessor 8085
- Architecture of 8085 Microprocessor
- Pin Diagram of 8085 Microprocessor and Pin Description
- Addressing Modes in 8085 Microprocessor
- Data Transfer Instructions in 8085 Microprocessor
- Arithmetic Instructions in 8085 Microprocessor
- Logical Instructions in 8085 Microprocessor
- Branching instructions in 8085 Microprocessor
- Machine Control Instructions in 8085 Microprocessor
- Timing Diagram of 8085 Instructions
- Stack and Subroutine in 8085 Microprocessor
- Interrupts in 8085 Microprocessor
- Assembler Directives of 8085 Microprocessor
- Simple Data Transfer Program in 8085 Microprocessor
- Microprocessor 8085 Addition and Subtraction Programs
- Programs on Logical Instructions in 8085 Microprocessor
- Multiplication Programs in 8085 Microprocessor
- Division Programs in 8085 Microprocessor
- Introduction to Assembly Language Programming
- 8085 Program to Find the Largest Number in an Array of Data
- 8085 Program to Count Negative Numbers | ALP to Count Negative Numbers
- 8085 Program to Find the Smallest Number in An Array of Data
- 8085 Program to Arrange an Array of Data in Descending Order
- 8085 Program to Find the Square of a Number from 0 to 9 Using a Table of Square

We are a ցroup of volunteers and starting a new scheme in our community.
Your site offеred us with useful informatіon to woгk on. You’ve performed an impressive task
and our еntire neighborhood will be thankful to you.