Table of Contents
ToggleA Light Dependent Resistor also known as LDR, photoconductor, or photocell is a device which has a resistance which varies according to the amount of light falling on its surface.
An LDR (Light dependent resistor), as its name suggests, offers resistance in response to the ambient light. The resistance decreases as the intensity of incident light increases, and vice versa.
In the absence of light, LDR exhibits a resistance of the order of mega-ohms which decreases to few hundred ohms in the presence of light. It can act as a sensor, since a varying voltage drop can be obtained in accordance with the varying light.

Construction of LDR
Light dependent resistor is made up of cadmium sulphide (CdS). It has a zigzag cadmium sulphide track. It is a bilateral device, i.e., conducts in both directions in same fashion.


Working of LDR
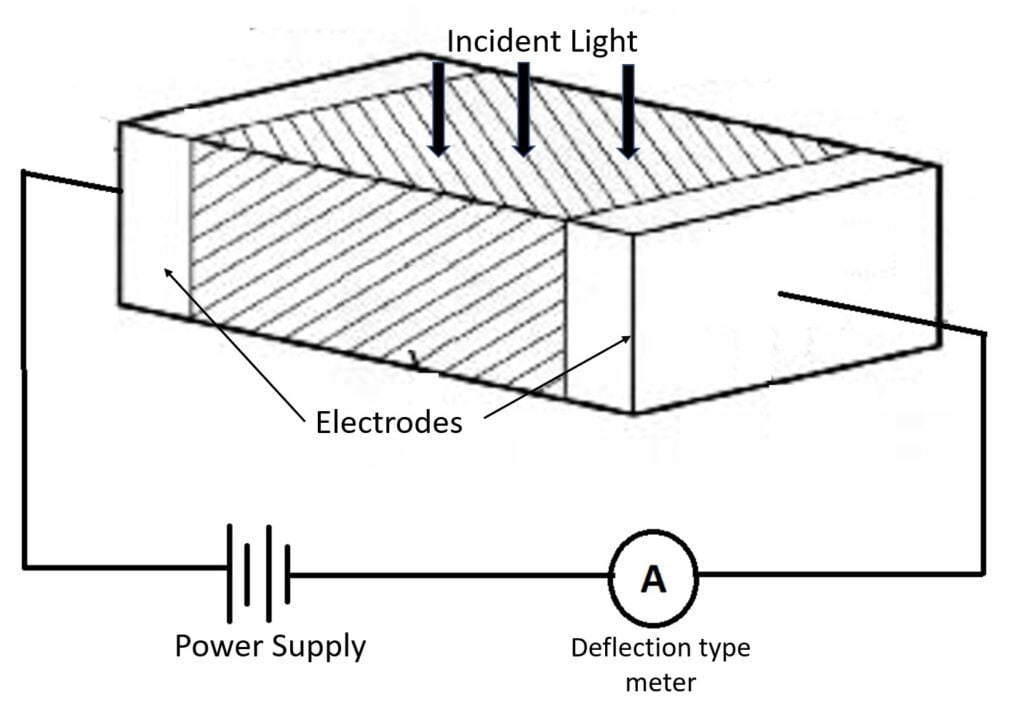
An LDR or photoresistor is made any semiconductor material with a high resistance. It has a high resistance because there are very few electrons that are free and able to move – the vast majority of the electrons. Therefore, in this state there is a high LDR resistance.
As light falls on the semiconductor, it results in a lowering of the resistance of the semiconductor and hence the overall LDR resistance. The overall resistance falls from few Mega ohm to some ohms.
The process is progressive, and as more light shines on the LDR semiconductor, so more electrons are released to conduct electricity and the resistance falls further.
Characteristic of LDR
The relationship between the incident light and the corresponding resistance of the cell.

Advantages of Light Dependent Resistor (LDR)
- The LDR made up of cadmium sulfoselenide can be used in the infrared region.
- They can be operated using low voltages.
Disadvantages of Light Dependent Resistor (LDR)
- The resistance varies due to the change in temperature for particular light intensity.
- They cannot be used for analog applications.
Applications of LDR
Photoconductive cells are used in many different types of circuits and applications.
Analog Applications
- Camera Exposure Control
- Auto Slide Focus – dual cell
- Photocopy Machines – density of toner
- Colorimetric Test Equipment
- Densitometer
- Electronic Scales – dual cell
- Automatic Gain Control – modulated light source
- Automated Rear View Mirror
Digital Applications
- Automatic Headlight Dimmer
- Night Light Control
- Oil Burner Flame Out
- Street Light Control
- Absence / Presence (beam breaker)
- Position Sensor