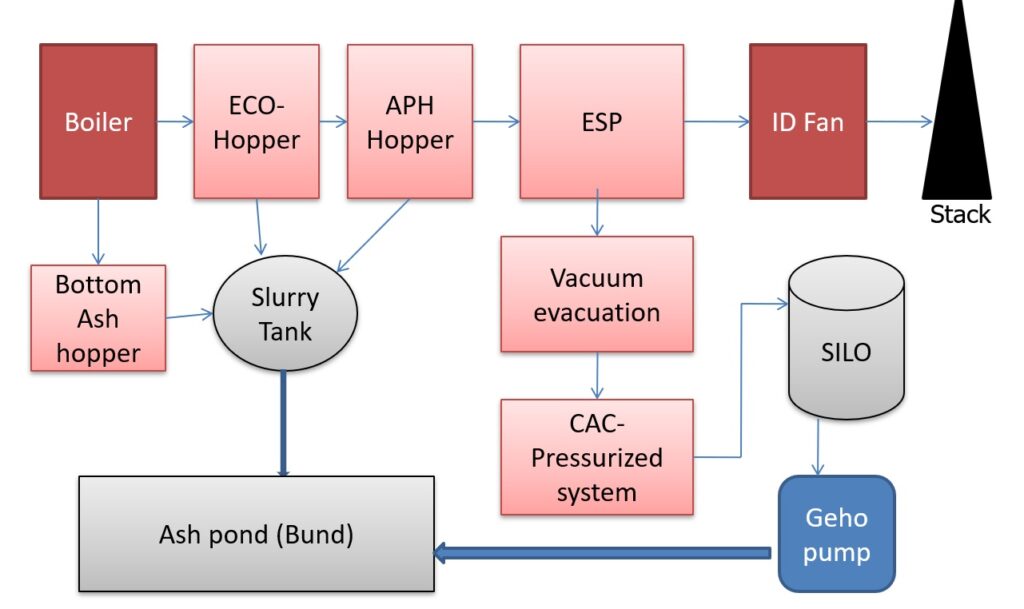
Table of Contents
ToggleThe Bowl Mill, also known as a pulverizer, incorporates the best features of various coal grinding systems, making it an efficient and reliable choice for pulverizing coal. Its main components include:
- Reduction Gearbox: Transmits power to the bowl and reduces the motor’s speed.
- Mill Side and Liner Assembly: Protects the structure from wear and tear.
- Primary Air and Mill Reject Chamber: Handles the air required for coal combustion and collects rejects.
- Revolving Bowl and Scraper: Facilitates coal grinding.
- Separator Body and Liner Assembly: Ensures the separation of finer particles from oversized material.
- Grinding Rolls and Journal Assembly: Presses coal against the bowl for pulverization.
- Classifier and Multiport Outlet Assembly: Regulates coal particle size and directs pulverized coal.
- Central Feed Pipe and Separating Inner Cone: Supplies raw coal to the bowl and returns oversized particles for further grinding.
- Pressure Spring Assembly: Applies necessary pressure for effective grinding.
A motor directly coupled to the worm shaft drives the reduction gear, which rotates the bowl at a reduced speed and transmits the power needed for pulverizing coal.
Operation of Bowl Mill
Grinding
Coal, typically around 1 inch in size, is fed into the bowl mill through the central feed pipe using the R.C. feeder. The centrifugal force generated by the rotating bowl moves the coal between the bull ring and spring-loaded grinding rolls.
The rolls, under spring pressure, crush the coal, which then moves to the bowl’s edge for further pulverization.
Transporting Fuel to the Furnace
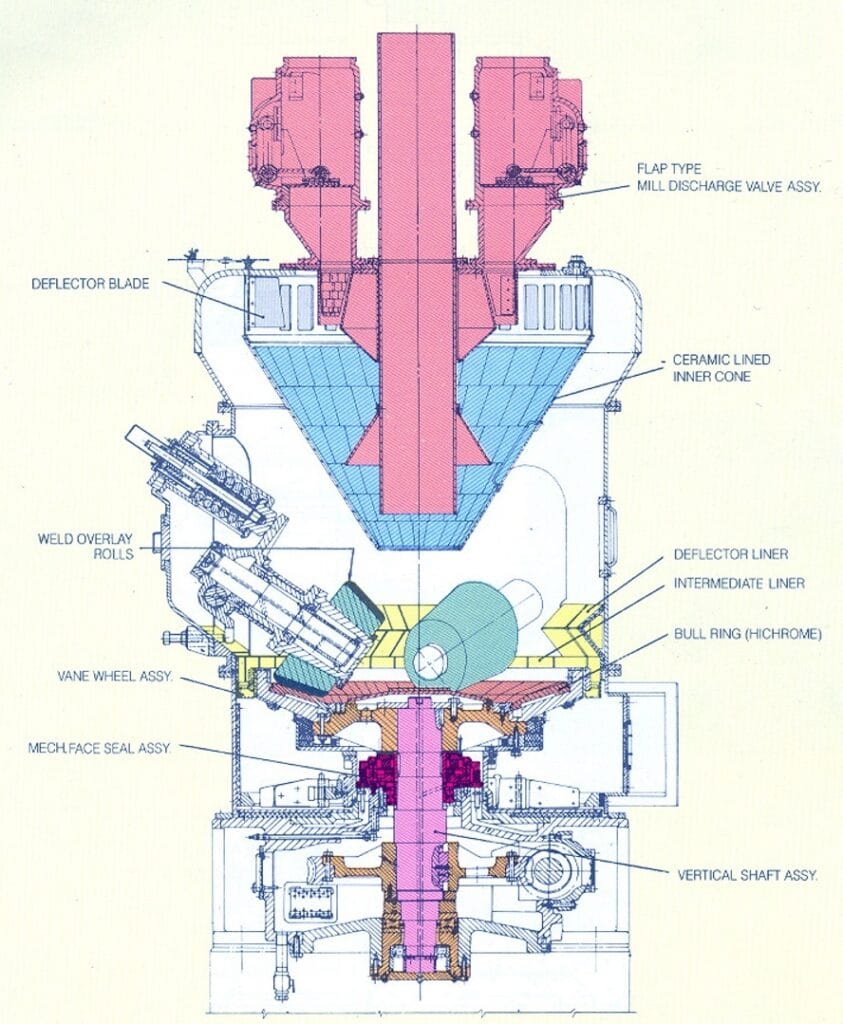
A mixture of hot and cold primary air enters below the bowl and sweeps around the separator body liners, carrying pulverized coal upwards. The following process ensures optimal delivery of fuel:
- Lighter pulverized particles are carried upward, while heavier particles hit the separator body liners and return to the bowl for additional grinding.
- Deflector blades impart a spinning motion to the coal-air mixture, controlling the coal’s particle size.
- Oversized particles are redirected down the inner cone for further grinding.
- Pulverized coal exits through multiport outlets, travels via fuel pipes, and reaches the furnace burners located at the boiler’s corners.
To ensure equal distribution, orifice plates are installed in the coal piping to balance flow resistance due to varying lengths and bends.
Reject Removal
Tramp materials like iron or other dense foreign objects are separated in the mill. Pivoted scrapers guide these materials to the tramp iron snout, where they exit via the pyrite hopper. This system includes gates for controlled removal of rejects during operation.

Temperature Control
Air temperature is critical for effective pulverization. The hot and cold air control dampers maintain the mill outlet temperature between 75°C to 85°C. Shutoff gates allow complete isolation of the mill for maintenance, ensuring operational safety.
Mill Air Flow
The mill should operate at its design airflow to prevent wear and ensure proper coal fineness. Deviations can result in coal rejects or excessive fineness, both of which reduce efficiency.
Sealing Arrangement
As a pressurized mill, sealing is essential to prevent coal dust from damaging internal components like bearings and gearboxes. A seal air system, comprising fans and filters, prevents contamination. Seal air can also be sourced from service air compressors if fans are unavailable.
Bearings and Lubrication
Bearings
- Worm Shaft Bearings: Radial and thrust bearings are oil-lubricated and housed within the reduction gearbox.
- Vertical Shaft Bearings: Both lower and upper bearings are lubricated through circulation systems powered by a pump.
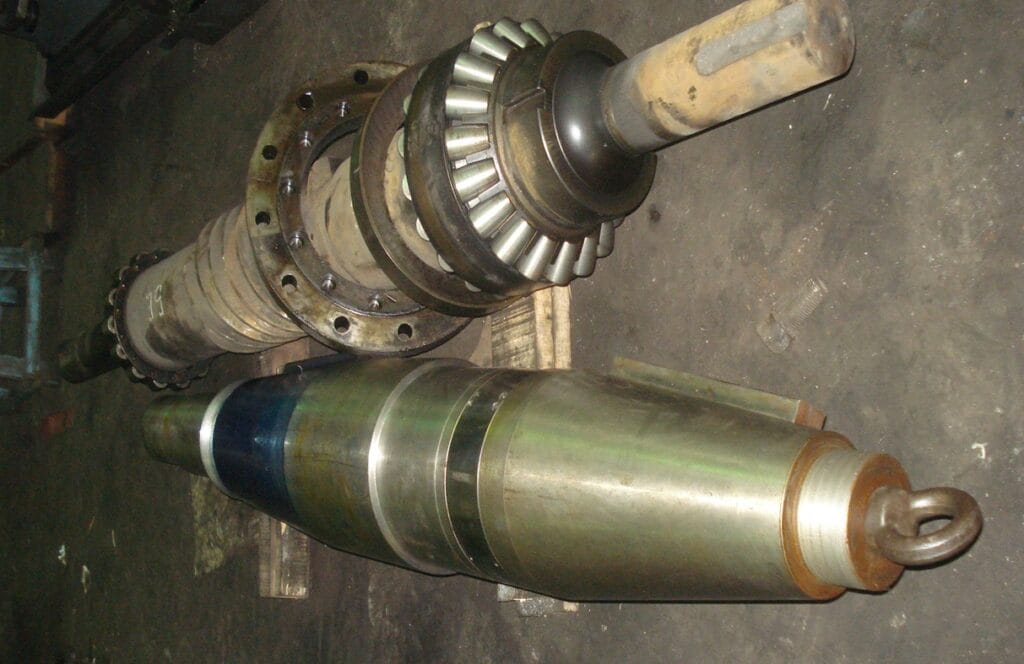

Lubrication
- Gearbox oil serves multiple functions, lubricating worm gears, bearings, and thrust components.
- Roller journals have a self-contained oil circulation system, ensuring continuous lubrication.
- Additional components like journal stop bolts, spring adjusting bolts, and couplings are grease-lubricated.
Oil Circulation
- A screw pump attached to the vertical shaft distributes oil to upper bearings and returns it to the gear housing.
- Pumping action ensures effective lubrication for all moving parts, maintaining operational integrity.
Oil Coolers
Tube-type oil coolers within the gear housing reduce oil temperatures during operation. A mechanical face seal arrangement prevents dust ingress into the gear casing.
The journals are equipped with seals to minimize oil wastage, while clean seal air prevents contamination in the bearings.
Mill Specifications
- Number of Mills per Boiler: 6
- Type: Pressurized
- Model: XRP 803
- Capacity: 39 tons/hour
- Coal Grindability: 55 HGI (Hardgrove Grindability Index)
- Moisture Content: Up to 12%
- Fineness: 70% through a 200-mesh screen
Motor Specifications:
- Power Rating: 340 kW
- Voltage: 6.6 kV (3-phase)
- Frequency: 50 Hz
- RPM: 980
- Rated Current: 41.7 A
Conclusion
- The Bowl Mill is a versatile and efficient coal pulverizer, ensuring optimal fuel preparation for thermal power generation. Its robust design, effective sealing, and advanced lubrication systems make it a reliable component in modern boiler systems.
- With precise control over temperature, air flow, and particle size, the Bowl Mill delivers consistent performance, reducing wear and maximizing efficiency.